Oral Thrush Treatment
- What is Oral Candidiasis?
- Symptoms of Oral Candidiasis
- Causes of Oral Candidiasis
- Risk factors in oral candidiasis
- Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
- Treatment of oral candidiasis
- Home remedies for oral candidiasis
- Prevention of oral candidiasis
- Conclusion
- Frequently asked questions about oral candidiasis
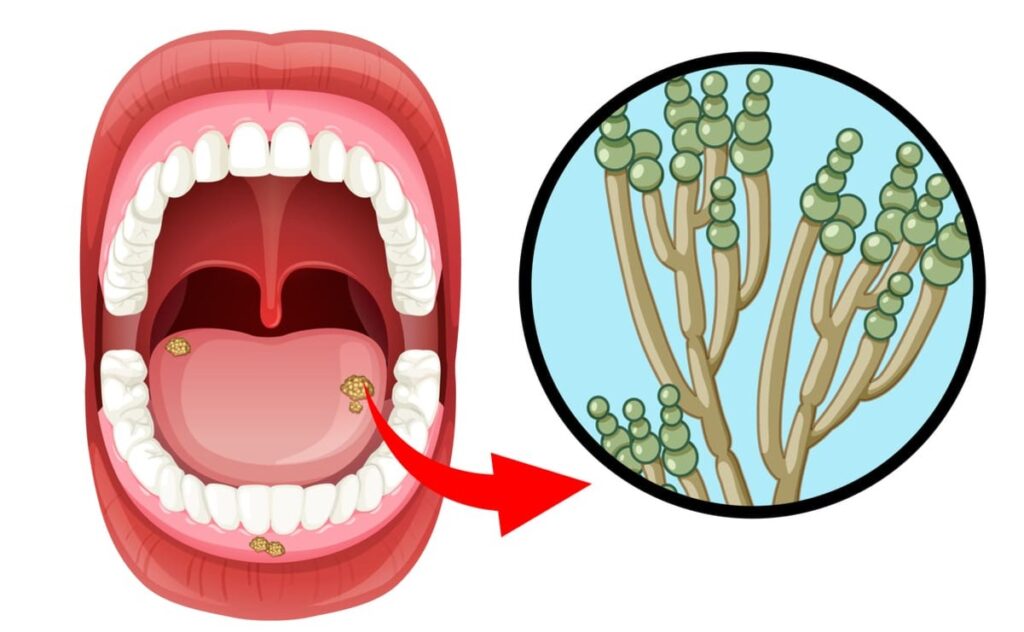
What is Oral Candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis, also called oral candidosis or even oral thrush, is an infection caused by a fungus called Candida albicans. This fungus is present in the oral cavity of many of us, but in a saprophytic form, without causing any pathology.
It is estimated that around 50% of the healthy population has this fungus in the oral cavity, being this percentage even higher as the age of the person advances, which causes this pathology to be increasingly important due to a life expectancy that continues to increase.

However, the presence of this fungus in the mouth is usually as a commensal species, that is, although it lives inside us, it does so in a balanced way, in homeostasis, together with the rest of fungi and bacteria that are part of the oral microbiota and thus can be there without causing any type of pathology, damage or infection.
The problem arises when an overgrowth of this fungus Candida albicans occurs, so that it ceases to live as a commensal to become a pathogenic species and cause infection.
Symptoms of Oral Candidiasis
It is an opportunistic infection, that is, the fungus takes advantage of a situation of an immune system that for some reason is weaker, to grow and exert its pathogenic effect causing the infection. It is then when the first symptoms of candidiasis in the mouth appear: whitish plaques on the tongue and the rest of the oral cavity. All this is often accompanied by difficulty in swallowing and pain.
Candida infections may be accompanied by lesions such as:
- Stomatitis (inflammation of the lips and mouth) that is aggravated by the use of dentures.
- Angular cheilitis. Commonly known as "cold sores", which appear at the corner of the lips.
- Median rhomboid glossitis. A reddish, colored patch on the back of the tongue.
Causes of Oral Candidiasis
There are different reasons why this fungus can cause candidiasis in the mouth:
- An immune system compromised by some type of treatment (e.g. chemotherapy treatment) so that Candida albicans becomes an opportunistic pathogen taking advantage of the changes that have occurred in the patient's microbiota as a consequence of these treatments.
- Stressful situations, related to the increase in cortisol that occurs in these situations and that result in a weakened immune system. Let us not forget the direct relationship between cortisol and stress.
- Pathologies involving deficient salivation (xerostomia), since there is a lower antibacterial and antifungal capacity of saliva itself, which is provided by proteins such as lysozyme, lactoferrin or sialoperoxidase.
- Use of dental prostheses or dentures, since their use causes a reduction of salivary flow in the area where the prosthesis adheres to the gum. In addition, anaerobic conditions are generated in this same area, with a low oxygen level that favors the presence of Candida albicans. The risk can even increase if the denture is not hygienically well maintained.
- The origin of this infection is also related to deficiencies of some vitamins (Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12 or Vitamin A) as well as iron deficiency.
- In the case of babies born with oral candidiasis, it usually originates from passage through the birth canal via a vagina infected with vaginal candidiasis.
- Treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (e.g. Fluticasone) may produce candidiasis due to a possible suppression of part of the cellular immunity.
- Diets rich in carbohydrates such as glucose, which favor Candida adhesion to epithelial cells.
- Treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics that alter the microbiota or oral flora and favor the growth of opportunistic species.
Risk factors in oral candidiasis
Some factors that increase the risk of developing oral candidiasis are:
- Advanced age.
- Prolonged use of antibiotics.
- Weakened immune systems.
- Use of inhaled steroids.
- Uncontrolled diabetes.
- Pregnancy.
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis is usually made by visual examination of the mouth and throat. In difficult cases, scrapings of the lesions may be taken for examination under a microscope.
Treatment of oral candidiasis
As it is a fungal infection, the most effective treatments are based on antifungal drugs such as nystatin, miconazole or fluconazole.
These drugs are usually applied in the form of oral suspension so that when administering it, try to keep it in the mouth as long as possible before swallowing the product. In this way, a longer time of direct contact between the drug and the fungus causing the infection is achieved.
If the patient also wears dentures, it is important that the dentures are washed or brushed using the drug to try to eliminate the presence of the fungus in the denture itself.
Treatment of oral candidiasis with probiotics
Probiotics are having a great boom in recent years. They are being used in Irritable Bowel Syndrome, in treatments for diarrhea, in intestinal discomfort. Part of the mechanism of action of probiotics is based on the displacement of the "good" bacteria of the organism (the probiotic) against pathogenic microorganisms.
In the case of oral candidiasis, one of the probiotics that have shown an improvement in the treatment of these fungi in the mouth is Bacillus clausii (1) where it was demonstrated that this probiotic reduces the signs and symptoms of this pathology when administered as an adjuvant to pharmacological treatment.
Other probiotics such as Lactobacillus paracasei and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus reuteri have demonstrated their ability to reduce the presence of Candida by modifying oral pH or other mechanisms of action (2).
Some probiotics that we can find on the Internet with these probiotic species with activity against oral candidiasis are:
Home remedies for oral candidiasis
There are really no home remedies for oral candidiasis. If we are suffering from this disease, what we have to do is to treat it by administering antifungals and/or make use of a probiotic treatment as well.
However, we can take some "home" measures that can help to make this fungus disappear from the mouth:
- Take a couple of yogurts a day. The probiotic load of yogurt can be very helpful in reducing the infectious load produced by the fungus.
- Extreme oral hygiene, even changing toothbrushes more frequently.
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol.
- Generate more saliva by chewing cardamom seeds or with chewing gum.
- Try to maintain a healthy lifestyle, with a healthy diet.
It is important to keep in mind that these remedies help provide temporary relief, but do not replace proper medical or pharmacological treatment.
Prevention of oral candidiasis
To prevent oral candidiasis, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene. Some preventive measures include:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Floss daily.
- Avoid excessive use of alcohol mouthwashes.
- Keep dentures clean and well adjusted.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugar and yeast-rich foods.
Conclusion
Oral candidiasis is a fungal infection that affects the mouth and throat. It is caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans. Common symptoms include velvety, whitish-white lesions, pain and difficulty swallowing.
It is important to seek appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing underlying conditions are also key to avoiding oral thrush.
Frequently asked questions about oral candidiasis
Is oral candidiasis contagious?
Oral candidiasis is not considered contagious, as Candida albicans is a common yeast found in many people without causing problems.
Is oral candidiasis common in infants?
Yes, thrush is common in infants. It is known as thrush and can cause white patches in the baby's mouth and tongue.
How can I prevent oral candidiasis if I wear dentures?
It is important to keep dentures clean and well-fitting. The dentist's instructions for proper care and cleaning should be followed.
Can oral candidiasis be cured?
Yes, oral candidiasis is treatable and in most cases resolves with proper treatment.
How long does it take to treat oral candidiasis?
The duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity of the infection. Generally, one to two weeks of treatment is needed to resolve oral candidiasis.
Can I have oral thrush if I have a healthy immune system?
Although less common, people with healthy immune systems can also develop oral candidiasis in certain circumstances, such as after taking broad-spectrum antibiotics.
What should I do if my baby has thrush?
If you suspect that your baby has oral thrush, it is important to consult a pediatrician for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Is oral candidiasis a sign of HIV infection?
Thrush can be a sign of immunodeficiency, including, but not limited to, HIV infection (the virus that causes the disease, AIDS). If you have concerns, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.
Can oral candidiasis recur after treatment?
Yes, oral candidiasis can recur in people prone to infection. It is important to follow your doctor's recommendations and maintain good oral hygiene to prevent recurrences.
Other Published Articles
[pt_view id="d1a5d19yu2"]
Si quieres conocer otros artículos parecidos a Oral Thrush Treatment puedes visitar la categoría Intestinal Health.
